Nuclear Medicine Cardiac Stress Test
What is a nuclear medicine (NM) cardiac stress test? A nuclear medicine (NM) cardiac stress test assesses the blood supply…
Read more
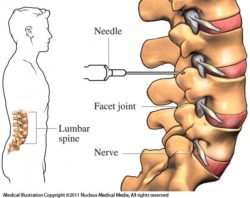
Anatomy of the lumbar spine
The spine is made up of bones called vertebrae. Between each vertebra is a ‘disc’ that allows the spine to be flexible. In between adjacent vertebrae, there is an opening on each side called a ‘foramen’, through which a nerve exits on its way to the buttock or leg. The nerve is surrounded by a ‘sleeve of fat’. Injection of corticosteroid (or ‘steroid’) and/or a local anaesthetic in the fat surrounding the nerve root is called nerve root sleeve injection. Corticosteroid medication decreases inflammation in the nerve root and will often reduce pain caused by nerve root inflammation, irritation of the nerve caused by arthritis or conditions such as disc degeneration or prolapsed disc (where the disc bulges).
Back and/or leg pain can come from compression of the nerve as it passes through the foramen. Compression can come from a damaged, bulging disc or from extra bone that grows as a response to arthritis in the joints between the vertebrae. Inflammation from scar tissue and swelling after surgery on the spine can also irritate the nerves in the lower back.
An injection of corticosteroid around the nerve root may alleviate the pain by reducing inflammation of the nerve. If the pain is suspected to come from a particular root, but it is not certain which one (especially in older people who may have root compression as a result of arthritis at a number of spinal levels), blocking the root with anaesthetic confirms or rules out that particular root as the cause. This can help in planning for future surgery. If surgery is a consideration, root sleeve injection may be used to relieve the pain before the surgery and can sometimes allow surgery to be delayed or avoided.
Because you will be lying on your stomach during the procedure and will be uncomfortable if your stomach is too full, it is advisable to limit food intake to a light meal only, up to 2 hours before the procedure. You should wear comfortable clothes that are easy to remove and leave jewellery at home. Please note that some of the disinfectant agents used during these procedures may stain light-coloured clothing.
When you make your appointment for the lumbar nerve root sleeve injection, you need to let the radiology clinic or department know if you are taking any blood thinning medication, such as warfarin, clopidogrel, dabigatran, prasugrel, dipyridamole or asasantin (for more information about these medications, go to NPS: www.nps.org.au/medicines).
Blood thinning medications may need to be stopped for a period of days, or your normal dose reduced, before this procedure is carried out. It is very important that you do not stop any of these medications or change the dose without consulting both the radiology clinic or department and your own doctor. They will give you specific instructions about when to stop and restart the medication. These drugs are usually prescribed to prevent stroke or heart attack so it is very important that you do not stop taking them without being instructed to do so by your doctor or the radiology practice, or both. Aspirin is usually not stopped.
A blood test may be required to check your blood clotting on the day of the procedure. Continue with pain medication and other medications as usual.
You may be monitored for 2–3 hours after the procedure, so please allow for this. You should arrange for someone to take you home after the procedure, as it is not advisable to drive for the rest of the day as you may have numbness, weakness or other temporary side-effects after the procedure.
You will be asked to change into a hospital gown in a changing room. You will be taken from the changing room into the computer tomography (CT) scanning room. You will be asked to lie on the CT scanning table on a thin plastic mattress. Plastic tape with small metal markers attached to it will be taped onto your back. The scanning table will be moved into the scanner and CT images or pictures of your spine will be taken. The tape with the markers is used to mark the spot, or level, in your spine where the needle for the lumbar nerve root sleeve injection will enter the skin. The spot will be marked on your skin with a pen and the tape removed.
The skin on the back is cleaned with antiseptic, which is usually very cold. The area is then covered with a sterile drape.
The radiologist (specialist doctor) or other specialist doctor carrying out the procedure will inject local anaesthetic into the skin and deeper tissues in your lower back. This will numb the skin and deeper tissues. This produces a pin prick and a stinging sensation that is uncomfortable for a few seconds. You will be awake and only the area where the lumbar nerve root sleeve injection is being carried out will be numb.
When the skin and muscles are numb, a thin spinal needle is then guided into place. CT scanning will be used to guide this so the doctor can confirm accurate placement of the needle.
When the needle is in the correct location, contrast medium (X-ray dye) may be injected to check the needle position. Contrast medium allows the X-ray to show the blood vessels more clearly on the images. A combination of corticosteroid and long-acting local anaesthetic is then injected into the tissue surrounding the nerve root.
The placement of the needle and injection of contrast into the foramen may produce some discomfort if the foramen is very tight from disc problems or a bony spur compressing the nerve root. The long-acting local anaesthetic very rapidly numbs the nerve. The area of the limb supplied by the nerve being treated goes numb, and the leg or foot may feel ‘dead’ for a while. This can be worrying when it happens, but you should be aware that the feeling and movement will recover soon.
The actual procedure itself takes approximately 15 minutes. You may be monitored after the procedure for 2–3 hours, so please allow for this. Monitoring occurs after the procedure to make sure any numbness, weakness or other temporary side-effects of the procedure have worn off before you go home. You may also have your blood pressure and breathing monitored after the procedure.
There are very few reports in the literature of permanent leg weakness and bladder function problems (paraplegia) after this procedure. This rare risk is thought to be caused by unintentional injection of one of the arteries that is a branch of an artery that supplies the spinal cord, and the use of particulate corticosteroids. It is thought that using non-particulate corticosteroids and checking that the needle is not in a vessel before injecting the steroid medication reduces or eliminates this complication.
Overall, the risks are minimal when carried out by experienced specialist doctors using CT image guidance. Approximately 7 in every 1000 patients will have some type of complication from this procedure and the severe complications (such as permanent nerve root damage) are rare.
The benefits of a lumbar nerve root sleeve injection include temporary or long-term relief of back and nerve root pain. Breaking the pain cycle aids in healing. Pain relief also makes you more comfortable, allowing the disc protrusion to shrink. This may delay or remove the need for surgery.
Lumbar nerve root sleeve injections are usually carried out by radiologists. The doctor carrying out the procedure needs to be appropriately trained in carrying out procedures using CT imaging and experienced in carrying out this procedure. Sometimes the procedure is carried out by pain management specialists, usually using X-ray imaging.
The procedure is carried out in a radiology practice, a radiology department in a hospital, an operating theatre with CT and X-ray imaging or an angiography suite. Wherever the procedure is carried out, there is a requirement for post-procedure observation beds and nursing care in order to identify and treat any of the complications that can sometimes occur after the procedure.
The time that it takes your doctor to receive a written report on theprocedure you have had will vary, depending on:
Please feel free to ask the private practice, clinic or hospital where you are having your procedure when your doctor is likely to have the written report.
It is important that you discuss the results with the doctor who referred you, either in person or on the telephone, so that they can explain what the results mean for you.
The procedure is effective if there is an accurate diagnosis as to the cause of the pain. If there is no nerve root compression or irritation at the level of the injection, there will be little or no response.
No. The most uncomfortable part of the procedure is the initial injection of local anaesthetic. After this, the rest of the procedure is usually not especially painful.
Page last modified on 26/7/2017.
RANZCR® is not aware that any person intends to act or rely upon the opinions, advices or information contained in this publication or of the manner in which it might be possible to do so. It issues no invitation to any person to act or rely upon such opinions, advices or information or any of them and it accepts no responsibility for any of them.
RANZCR® intends by this statement to exclude liability for any such opinions, advices or information. The content of this publication is not intended as a substitute for medical advice. It is designed to support, not replace, the relationship that exists between a patient and his/her doctor. Some of the tests and procedures included in this publication may not be available at all radiology providers.
RANZCR® recommends that any specific questions regarding any procedure be discussed with a person's family doctor or medical specialist. Whilst every effort is made to ensure the accuracy of the information contained in this publication, RANZCR®, its Board, officers and employees assume no responsibility for its content, use, or interpretation. Each person should rely on their own inquires before making decisions that touch their own interests.